One of the consequences of COVID-19 is the recognition that many tasks can be done from home. But anything that can done remotely, can be done from abroad.
Given large salary differences between white collar workers across countries, it would make sense for value chains to try to exploit them. This opens an opportunity for Colombia to further promote its integration into the world global value chains and access new markets.
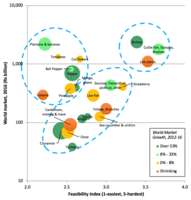
This paper explores the possibility of exporting teleworkable services from Colombia. The goal is to provide useful information to guide strategic interventions to speed-up the development of such service industries in Colombia.
We first introduce a definition of teleworkable jobs and describe its occupations and industries along different dimensions. We show that there are many teleworkable jobs in the US, representing a significant share of industry costs. Then, we show that many industries intensive in teleworkable jobs are currently traded across borders. To quantify Colombia’s advantage providing teleworkable services, we study the cost structure of industries and quantify the potential savings in overall costs if the tasks were performed by Colombians. Given Colombia’s current presence and the density around teleworkable industries we can calculate a proxy of the latent advantage in teleworkable services. We propose an index that summarize these dimensions and rank the potential gains from including telework from Colombia in an industry. We end with a set of policy recommendations to move this agenda forward.